Blog
- Home
- Blog
How to Choose the Right High Flow Hydraulic Pump for Your Project
Choosing the right high flow hydraulic pump for your project is a critical decision that can impact overall efficiency and performance. According to industry expert John Smith, a renowned hydraulic systems engineer, "Selecting the appropriate high flow hydraulic pump requires a thorough understanding of your project’s demands and specifications." Understanding these factors is essential to ensure optimal functioning and to meet the specific hydraulic needs of your application.
High flow hydraulic pumps are designed to deliver significant amounts of fluid, making them ideal for projects that require rapid movements or heavy lifting. However, with the myriad of options available, from variable displacement to fixed displacement pumps, it becomes crucial to assess what features are necessary for your unique requirements. Experts emphasize that the key to making the right choice lies in evaluating system requirements, desired flow rates, and the operating conditions that will influence pump performance.
Overall, making an informed decision on a high flow hydraulic pump means taking the time to analyze both the technical details and the operational environment of your project. By engaging with industry professionals and conducting thorough research, you can ensure that your selection aligns perfectly with your project's goals and enhances overall productivity.

Understanding High Flow Hydraulic Pumps and Their Applications
When selecting a high flow hydraulic pump for a project, it's essential to understand their diverse applications across various industries. High flow hydraulic pumps are designed to deliver large volumes of hydraulic fluid at relatively high pressures, making them crucial in applications such as construction, manufacturing, and material handling. According to the Hydraulic Institute, the demand for hydraulic pumps is projected to grow at a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 5.6% from 2020 to 2027, primarily driven by increased industrial automation and machinery efficiency.
These pumps can typically handle flow rates ranging from 40 to 100 gallons per minute (GPM), significantly impacting operational productivity. For instance, in construction, high flow hydraulic pumps are often used in excavators and wheel loaders, enabling faster cycle times and enhanced performance efficiency. Additionally, the adaptability of these pumps to various systems makes them viable in niche applications such as forestry and agriculture, where they power equipment like log splitters and seeders. Industry studies indicate that the effective use of high flow systems can lead to a 20% increase in operational efficiency, showcasing their importance in optimizing workflows across sectors.
Key Factors to Consider When Selecting a Hydraulic Pump
When selecting a high flow hydraulic pump for your project, there are several key factors to consider to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. First and foremost, understanding the required flow rate for your specific application is crucial. This involves calculating the system's demands and ensuring that the chosen pump can meet or exceed these requirements. Consider the application’s peak flow needs as well as the continuous operating flow to provide a balanced approach to performance.
Another significant factor is the hydraulic pump design and its compatibility with the intended system. Different designs, such as gear, vane, or piston pumps, offer varying benefits in terms of efficiency and maintenance needs. Selecting the right type involves assessing the pressure range, the viscosity of the hydraulic fluid, and the overall system layout. Additionally, the installation space and accessibility for maintenance should factor into your decision, as some pump designs may require more room or maintenance than others. By thoroughly evaluating these elements, you can make a well-informed choice that leads to successful project execution.
How to Choose the Right High Flow Hydraulic Pump for Your Project
| Factor | Description | Importance | Recommendations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Rate | The volume of fluid the pump can move per unit of time. | High | Ensure the pump meets or exceeds the project’s required flow rate. |
| Pressure Rating | Maximum pressure the pump can handle without failure. | High | Select a pump with a pressure rating at least 10% higher than required. |
| Pump Type | Different designs used for various applications (gear, vane, piston). | Medium | Choose based on application requirements (e.g., gear pumps for high viscosity). |
| Size and Weight | Physical dimensions and weight can affect installation. | Medium | Consider space and support structures. |
| Efficiency | How effectively the pump converts motor energy into hydraulic energy. | High | Select a pump with a high efficiency rating for lower operating costs. |
| Material | The construction material affects durability and compatibility. | Medium | Ensure materials are compatible with the hydraulic fluid used. |
| Cost | The purchase price and total lifetime costs, including maintenance. | High | Balance initial cost with quality and long-term performance. |
Evaluating Flow Rate and Pressure Requirements for Your Project
When selecting a high flow hydraulic pump, understanding your project's flow rate and pressure requirements is crucial. The flow rate, typically measured in gallons per minute (GPM) or liters per minute (LPM), indicates how much hydraulic fluid the pump can deliver. Your project's specific needs will dictate the ideal flow rate. For instance, heavy machinery operations may require higher flow rates to ensure efficient and swift performance, while smaller systems might function well with lower rates.
Tip: Always consider the peak flow demands of your system; it’s better to have a pump that exceeds your requirements than one that falls short.
Pressure requirements also play a significant role in pump selection. This is expressed as pounds per square inch (PSI) and determines the pump's capability to overcome system resistance. Assess the maximum pressure needed for your application and choose a pump that can comfortably exceed this requirement to avoid system failure.
Tip: Regularly evaluate the operational environment, including temperature and viscosity of the hydraulic fluid, as these factors can significantly influence both flow rate and pressure performance. Choosing a pump that is compatible with the specific conditions of your project can lead to enhanced efficiency and reliability.
Assessing Pump Compatibility with Hydraulic Systems and Components
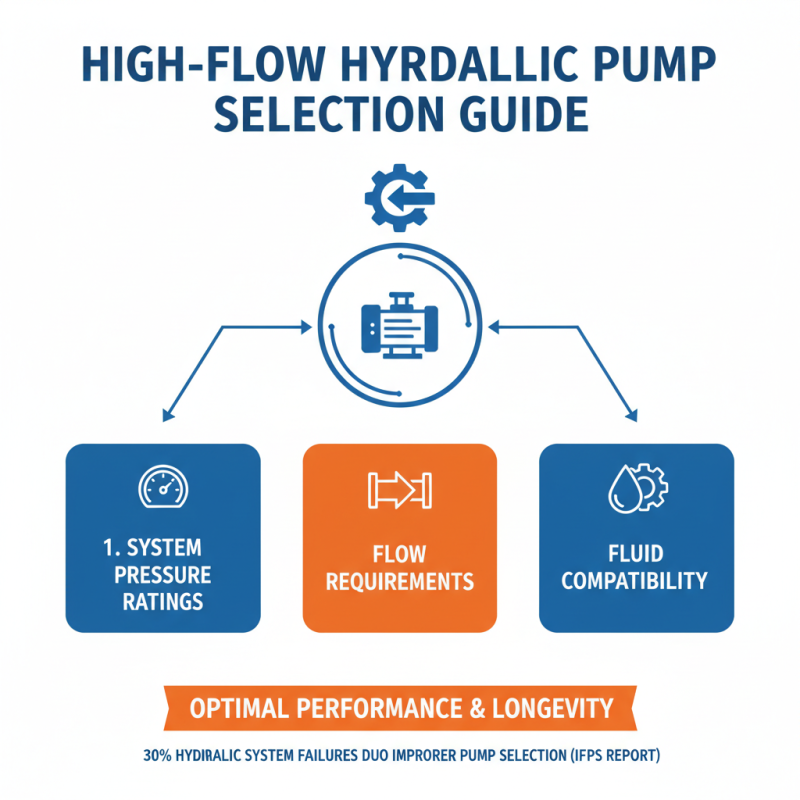
When selecting a high flow hydraulic pump, it's crucial to assess its compatibility with existing hydraulic systems and components. According to a report by the International Fluid Power Society, nearly 30% of hydraulic system failures stem from improper pump selection. Key factors to consider include system pressure ratings, flow requirements, and compatibility with hydraulic fluids. Ensuring that the pump can operate within the existing hydraulic pressure range and match the system's flow demands is vital for optimal performance and longevity.
Tips for Compatibility:
1. Always refer to the specifications of the hydraulic system to determine the required flow rate and pressure levels. Utilizing a pump that exceeds these requirements can lead to excessive wear or catastrophic failure.
2. Consider the compatibility of hydraulic fluids. A recent study published in the Journal of Hydraulic Engineering shows that using incompatible fluids can diminish pump efficiency by as much as 25%, leading to increased maintenance costs and system downtime.
Moreover, it’s essential to check the pump's physical dimensions to ensure it fits within the installation space and aligns with other components like tubing and fittings. An accurate assessment of these aspects will help in achieving a smooth integration of the pump into your hydraulic system.
Analyzing Cost and Maintenance Considerations for Hydraulic Pumps
When selecting a high flow hydraulic pump, cost and maintenance considerations play a crucial role in determining its overall efficiency and effectiveness for your project. According to a study by the International Fluid Power Society, maintenance costs can account for up to 30% of the total operational expenses of hydraulic systems. This highlights the need for thorough analysis and understanding of potential maintenance requirements before making a decision. High-performance pumps often have advanced features that can minimize wear and tear but may come with a higher initial price tag. Therefore, it is essential to balance initial investment with long-term savings on maintenance.
Additionally, assessing the long-term operational costs associated with different pumps can lead to significant savings. A report by the Hydraulic Institute indicates that the total cost of ownership (TCO) for hydraulic pumps—including installation, operation, maintenance, and eventual replacement—can vary greatly depending on the model and technology employed. Choosing a product with robust construction and lower energy consumption not only reduces the likelihood of breakdowns but can also lead to lower energy costs over time. Ultimately, understanding these cost implications will guide you in selecting a hydraulic pump that not only meets your performance requirements but also aligns with your budgetary constraints and maintenance capabilities.
High Flow Hydraulic Pump Cost and Maintenance Analysis
Related Posts
-
Top 10 High Flow Hydraulic Pumps for Enhanced Performance and Efficiency
-

10 Tips for Maximizing Efficiency with High Pressure Hydraulic Pumps in Industrial Settings
-

Unlocking Efficiency: How High Pressure Pumps Revolutionize Industrial Processes
-

How to Optimize Pump Water Efficiency for Sustainable Resource Management
-

Unlocking Efficiency: The Significant Advantages of Plunger Metering Pumps in Process Industries
-

Top 10 Best High Pressure Chemical Pumps for Optimal Performance
